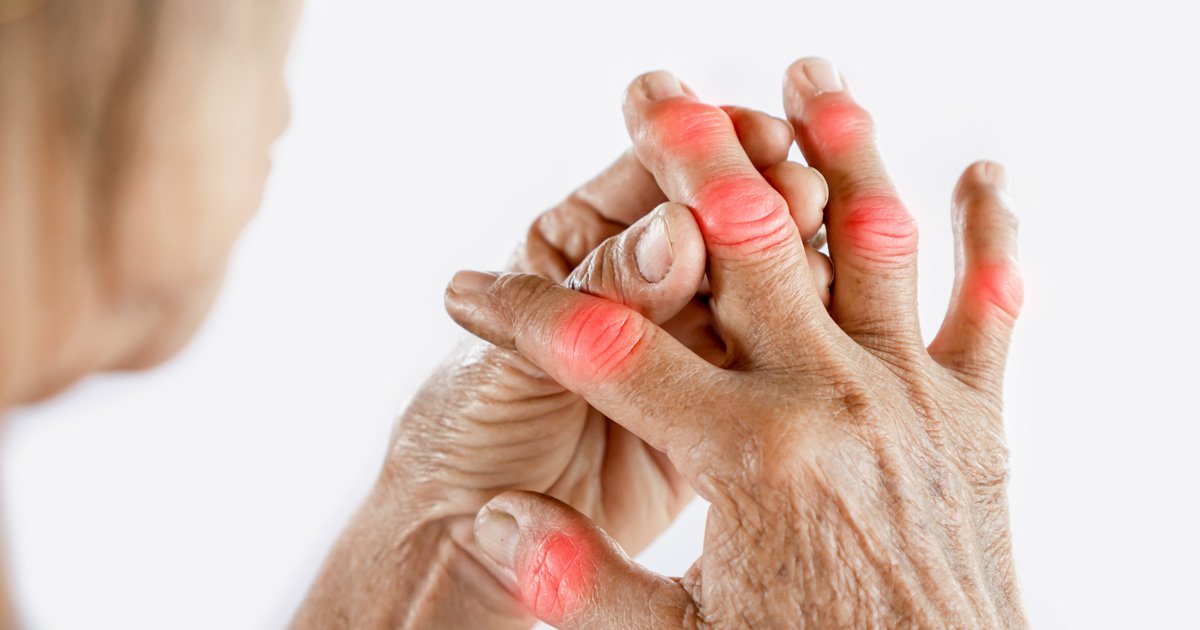
What is rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is basically a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease wherein your immune system mistakenly attacks your own body’s tissues. RA strikes usually many joints at once, and commonly takes a toll on joints in the hands, wrists, and knees.
“Rheumatoid arthritis affects the lining of your joints, causing a painful swelling that can eventually result in bone damage and joint deformity. RA can also affect other tissues throughout the body and cause problems in organs such as skin, lungs, heart, blood vessels and eyes,” says Dr Sumit Batra, Director Orthopaedics and Joint Replacement, Marengo QRG Hospital, Faridabad.
What are the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis
There is no cure of this disease and the symptoms may vary in severity in patients of rheumatoid arthritis. They may get worse at times (known as flares); or get better (known as remission).
Signs and symptoms of RA include:
– Pain, or swelling in multiple joints
– Joint stiffness that is usually worse in the mornings and after inactivity
– Weight loss
– Fatigue or tiredness, Weakness
– Early disease usually starts with small joints of hands which later can involve other joints e.g., Knee, ankles, elbow and shoulder.
– About 40% of patients also experience symptoms related to skin, lungs, heart or eyes.
What causes rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is the result of an immune response in which the body’s immune system attacks its own healthy cells.
Risk factors include:
– Genetics: People born with specific genes are more likely to develop RA. These genes are known as HLA (human leukocyte antigen) class II genotypes.
– Sex: It affects 3% of women and 1% of men.
– Smoking and Obesity can increase the risk of developing RA.
– Women who have never given birth may be at greater risk of developing RA.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is done by reviewing symptoms, conducting a physical examination, and doing X-rays and lab tests. Special blood tests include positive Rheumatoid factor and Anti CCP antibodies.
Treatment
There is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis. The symptoms and quality of life of the patient can be improved with medication or surgery.
Medication: The disease can be controlled with medications that include: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), steroids and specific drugs known as DMARDs (Disease modifying antirheumatic drugs). These drugs can be recommended to help slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and save the joints and other tissues from permanent damage. Common DMARDs include methotrexate, leflunomide, hydroxychloroquine and sulfasalazine and Biologic agents.
Surgery: Sometimes surgery can be useful in reducing pain and improving function. Surgical options include Synovectomy (removal of joint lining), Joint fusion or Total joint replacement.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Pregnancy
“Many women with rheumatoid arthritis report improvement in their symptoms during pregnancy. Many also report a worsening of symptoms after childbirth, usually within the first three months. Women who suffer from rheumatoid arthritis have lower chances of getting pregnant with assisted reproductive technology such as IVF,” says Dr Sumit Batra.